Triangle Calculator SSS
The Law of Cosines states that:
c2 = a2 + b2 - 2ab * cos γ
Where c is the length of the side opposite angle C, a and b are the lengths of the other two sides, and C is the measure of the angle opposite side c. You can use this formula to find the measure of each angle by plugging in the known side lengths and solving for the angle.
Once you have the measures of the angles, you can use trigonometric functions like Sine and Cosine to find the area of the triangle.
Another way to find the area of a triangle when you know the lengths of all 3 sides is to use Heron's Formula. Heron's formula states that:
Area = √(s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c))
Where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, which is the sum of the three side lengths divided by 2, and a, b, and c are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Heron's formula allows you to find the area of a triangle even if you don't know the measures of the angles, and it works for any type of triangle, whether it's acute, right or obtuse.
If you know the special property of a triangle, use an equilateral triangle, isosceles or right triangle calculator.
Mathematical problems using the SSS theorem for triangle:
- Sss triangle
 Calculate the area and heights in the triangle ABC by sides a = 8cm, b = 11cm, c = 12cm
Calculate the area and heights in the triangle ABC by sides a = 8cm, b = 11cm, c = 12cm - Sss triangle 2
 Construct triangle ABC in which |AB|=5cm, |AC|=6cm and |BC|=9cm
Construct triangle ABC in which |AB|=5cm, |AC|=6cm and |BC|=9cm - Medians
 Calculate the sides of a right triangle if the length of the medians to the legs are ta = 25 cm and tb=30 cm.
Calculate the sides of a right triangle if the length of the medians to the legs are ta = 25 cm and tb=30 cm. - Triangle SSS
 Calculate the perimeter and area of a triangle ABC if a=45, b=30, and c=50.
Calculate the perimeter and area of a triangle ABC if a=45, b=30, and c=50. - RT sides
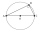 Find the sides of a rectangular triangle if legs a + b = 17cm and the radius of the written circle ρ = 2cm.
Find the sides of a rectangular triangle if legs a + b = 17cm and the radius of the written circle ρ = 2cm. - Hypotenuse and legs
 A right triangle with hypotenuse c=25 dm is given. Calculate the length of the unknown side, given: side a=15 dm. Find the area of this triangle. Sketch the triangle and describe all its vertices and sides correctly.
A right triangle with hypotenuse c=25 dm is given. Calculate the length of the unknown side, given: side a=15 dm. Find the area of this triangle. Sketch the triangle and describe all its vertices and sides correctly. - Rectangular triangles
 The lengths of the corresponding sides of two rectangular triangles are in the ratio 2:5. At what ratio are medians relevant to hypotenuse these right triangles? At what ratio are the areas of these triangles? A smaller rectangular triangle has legs 6 and
The lengths of the corresponding sides of two rectangular triangles are in the ratio 2:5. At what ratio are medians relevant to hypotenuse these right triangles? At what ratio are the areas of these triangles? A smaller rectangular triangle has legs 6 and - Lunes of Hippocrates
 Calculate the sum of the area of the so-called Hippocratic lunas, which were cut above the legs of a right triangle (a = 6cm, b = 8cm). Instructions: First, calculate the area of the semicircles above all sides of the ABC triangle. Compare the sum of the
Calculate the sum of the area of the so-called Hippocratic lunas, which were cut above the legs of a right triangle (a = 6cm, b = 8cm). Instructions: First, calculate the area of the semicircles above all sides of the ABC triangle. Compare the sum of the - Area of RT 2
 Calculate the area of a right triangle whose legs have a length of 9 cm and 6.4 cm.
Calculate the area of a right triangle whose legs have a length of 9 cm and 6.4 cm. - Right triangle
 Right triangle legs have lengths 71 dm and 919 mm. Calculate the area of this triangle.
Right triangle legs have lengths 71 dm and 919 mm. Calculate the area of this triangle. - An isosceles 2
 An isosceles triangular frame has a measure of 72 meters on its legs and 18 meters on its base. Find the perimeter of the frame.
An isosceles triangular frame has a measure of 72 meters on its legs and 18 meters on its base. Find the perimeter of the frame. - Catheti
 The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 35, and the sum of legs is 49. Calculate the length of its legs.
The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 35, and the sum of legs is 49. Calculate the length of its legs. - Right triangle - legs
 Calculate the area of a right-angled triangle ABC with a=15 cm, b=1.7 dm.
Calculate the area of a right-angled triangle ABC with a=15 cm, b=1.7 dm. - OPT
 What is the perimeter of a right triangle with the legs 11 cm and 24 cm long?
What is the perimeter of a right triangle with the legs 11 cm and 24 cm long? - Circumscribing
 Find the radius of the circumscribed circle to the right triangle with legs 6 cm and 3 cm.
Find the radius of the circumscribed circle to the right triangle with legs 6 cm and 3 cm.
more triangle problems »
Also, take a look at our friend's collection of math problems and questions!
- triangle
- right triangle
- Heron's formula
- The Law of Sines
- The Law of Cosines
- Pythagorean theorem
- triangle inequality
- similarity of triangles
- The right triangle altitude theorem
